- 4.6.0.0
Related Products
CRA series、E6
Release Versions:
- Controller Firmware:4.6.0.0
- Software
- DobotStudio Pro(PC):4.6.0.0
- DobotStudio Pro(Android):4.6.0.0
- DobotStudio Pro(Teach Pendant):4.6.0.0
- DobotStudio Pro(iOS):4.6.0.0
- Teach Pendant:4.6.0.0
- CRA Slave Firmware
- Safety controller:1.4.1.7
- Servo:6.1.9.1
- Energy Feedback Board:1.1.4.0
- Universal IO:3.0.3.4
- E6 Slave Firmware
- Robot Maintenance Tool:2.0.0
- Virtual controller: include
Compatibility
- The version changes the original collision level to a safety limit level with more quantified parameter indicators, and different levels constrain different robot speeds. Therefore, when the setting exceeding safety level 2 is used, it is possible to observe changes in robot cycle time. If you need to be able to maintain a higher cycle time even with a higher security level, please use the custom option.
- By default, the torque constraint function is enabled in the version, which can maximize the work cycle of the robot and ensure that the torque of each joint does not exceed the use limit. However, when moving near the singularity, the work cycle may be slow.
- The trajectory recovery function is added in version. When the robot triggers the alarm, please pay attantion that the robot will enter the suspended state. At this time, if the program or Settings need to be modified, the program needs to be stopped first.
Safety
The safety functions and safety design of CRA are systematically optimized in this version, aiming to further improve the safety of robot use and enable cooperative robots to work stably in a variety of complex environments.
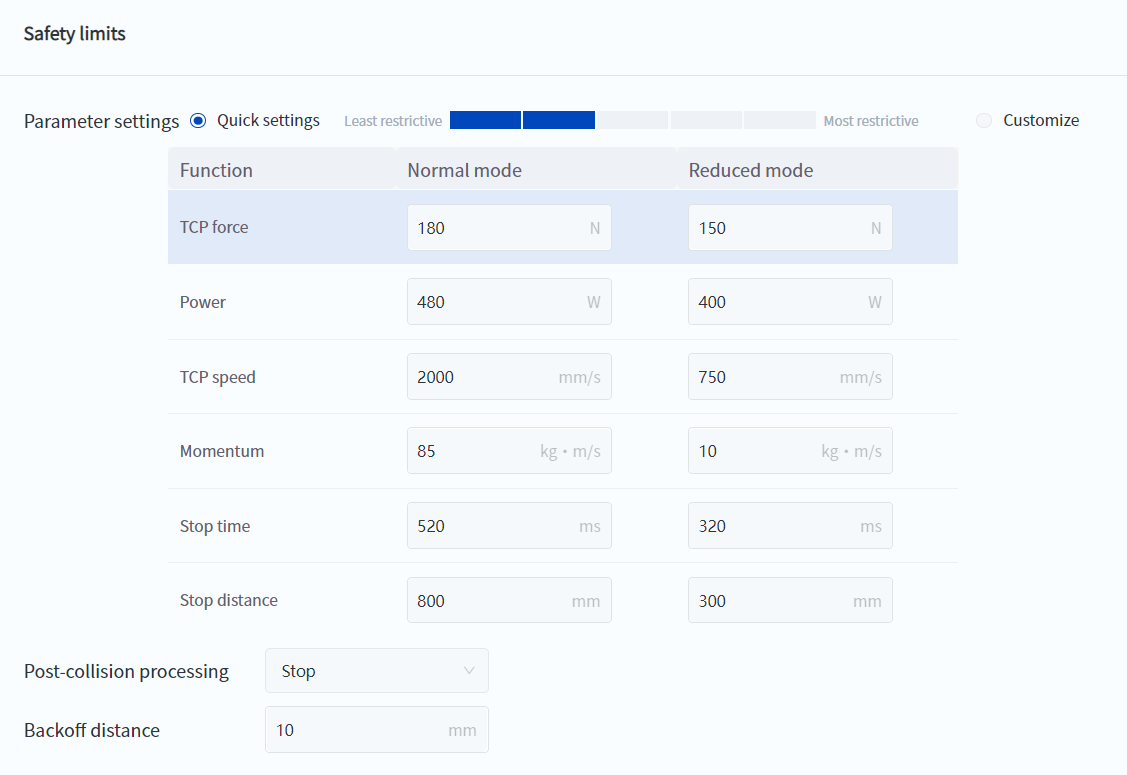
- Safety Limits
- Change the collision level setting to a more quantitative safety limit setting (TCP force, power, momentum, etc.), and these limits can set the values in the robot's normal mode and reduced mode respectively.
- It should be noted that TCP force and power limits mainly affect the robot's collision detection sensitivity. TCP speed, momentum, stop time, and stop distance limits mainly constrain the robot's maximum movement speed. Therefore, if the robot speed is found to be slower than expected during use, it may be due to unreasonable settings of these parameters.
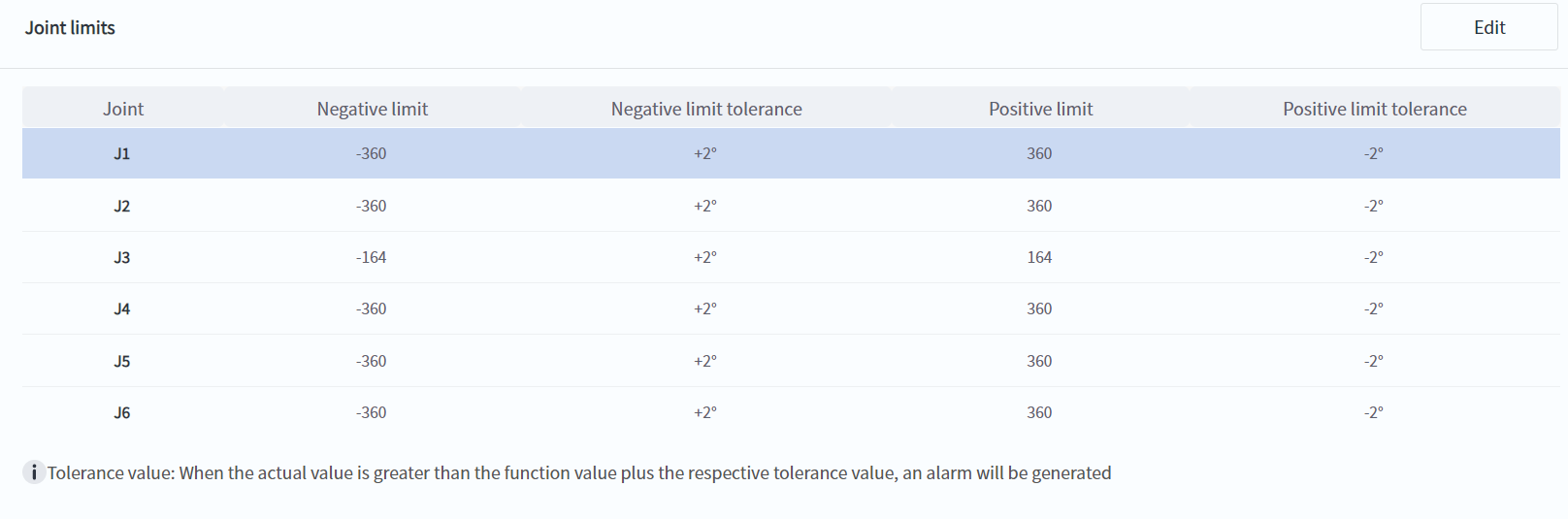
- Joint Limits
- The value of the joint soft limit can be changed through DobotStudio Pro. It should be noted that the actual joint motion range of the robot is constrained to the positive and negative limit setting values plus the tolerance.
- Safety checksum
- You can view the robot's safety checksum on the status page. This parameter is uniquely determined by the safety parameters. Any modification of the safety parameters will cause the safety checksum to change.
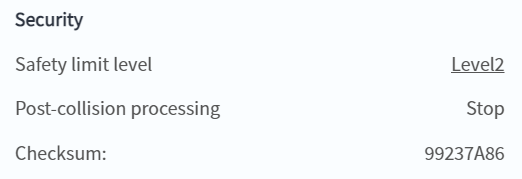
- After the version upgrade or execution file import, the safety checksum may change when the robot is turned on. Please handle it according to the actual situation.
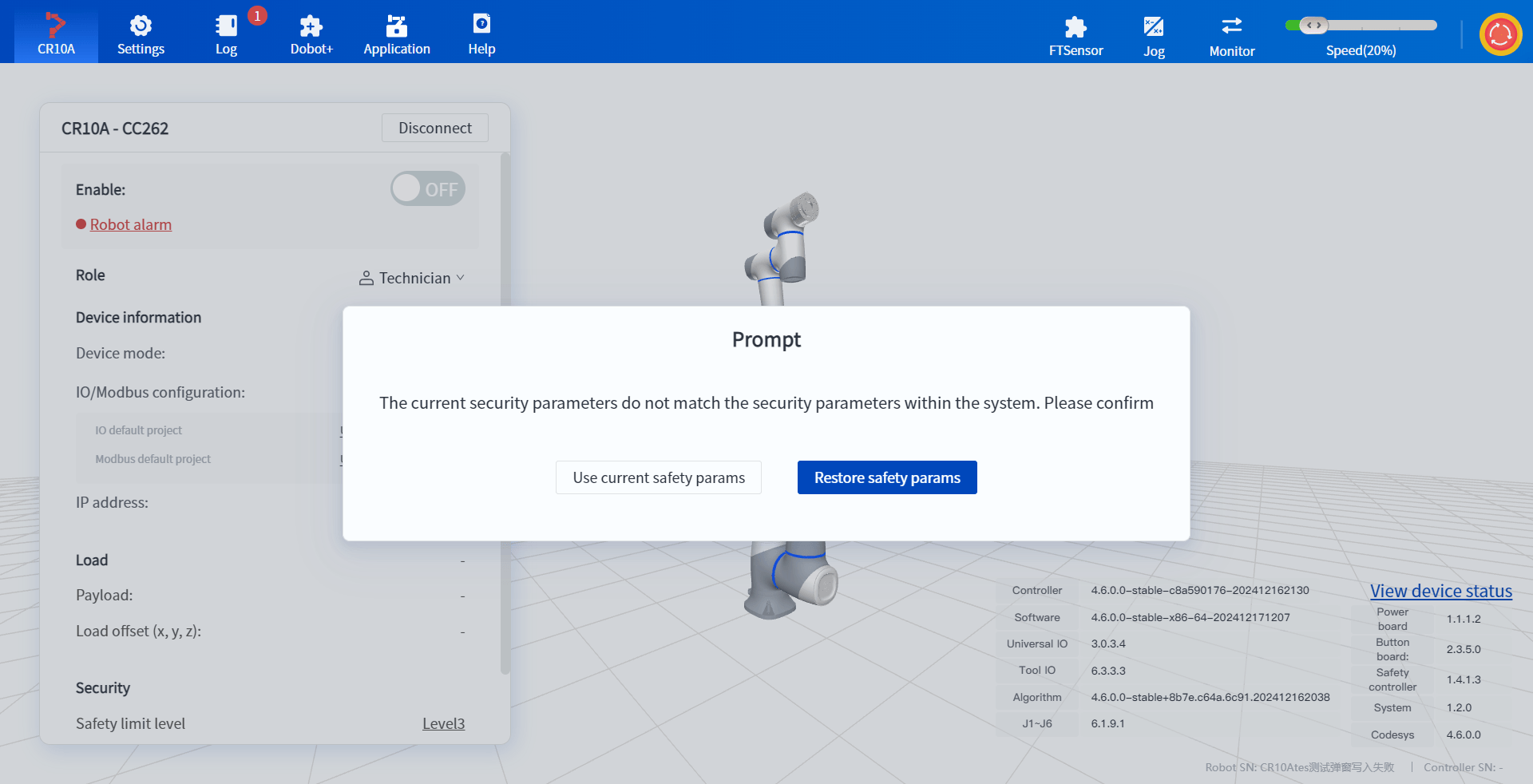
- Recovery mode
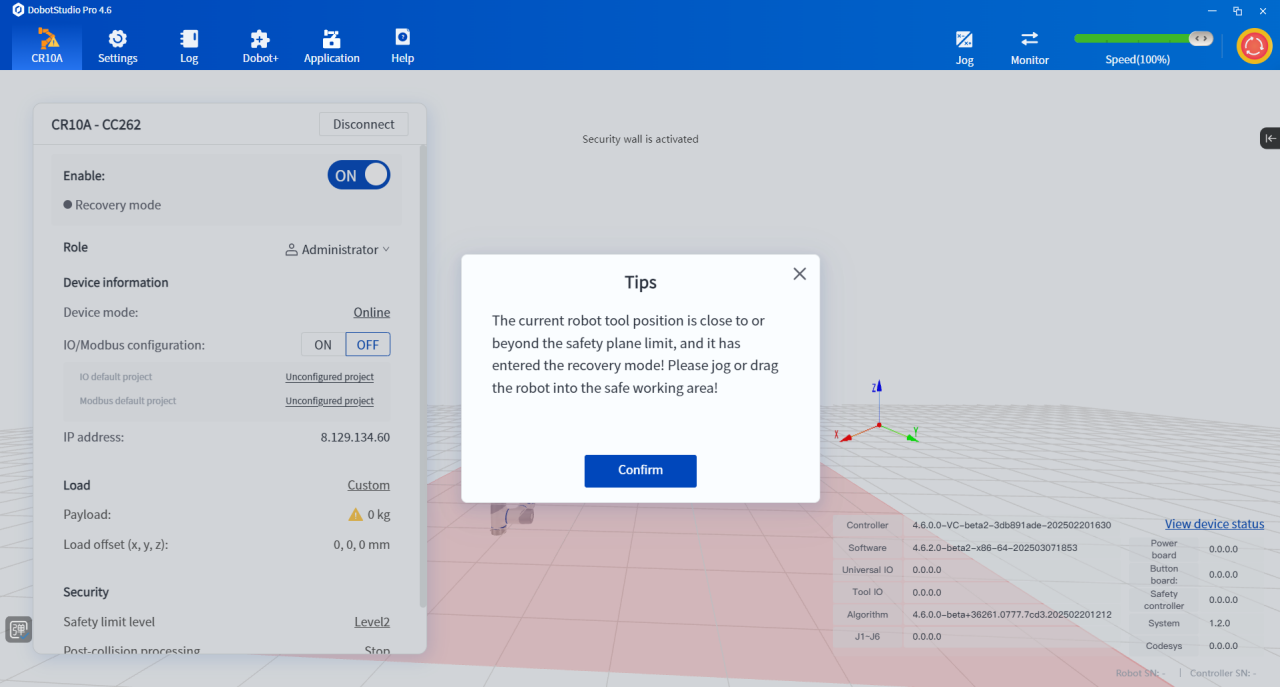
- When the robot violates the position limit (such as exceeding the joint soft limit, exceeding the safety wall or safety area), it will automatically enter a state called "recovery mode". In this state, the robot will adopt more stringent safety restrictions and can only be moved or dragged, so that the user can safely remove the robot from the dangerous position.
- When the robot is moved or dragged to a safe position, it will automatically exit the recovery mode and the robot function will return to normal.
- In recovery mode, the robot status light is orange and the corresponding prompt appears in the DobotStudio Pro software interface, which will help you reasonably judge the current safety status of the robot.
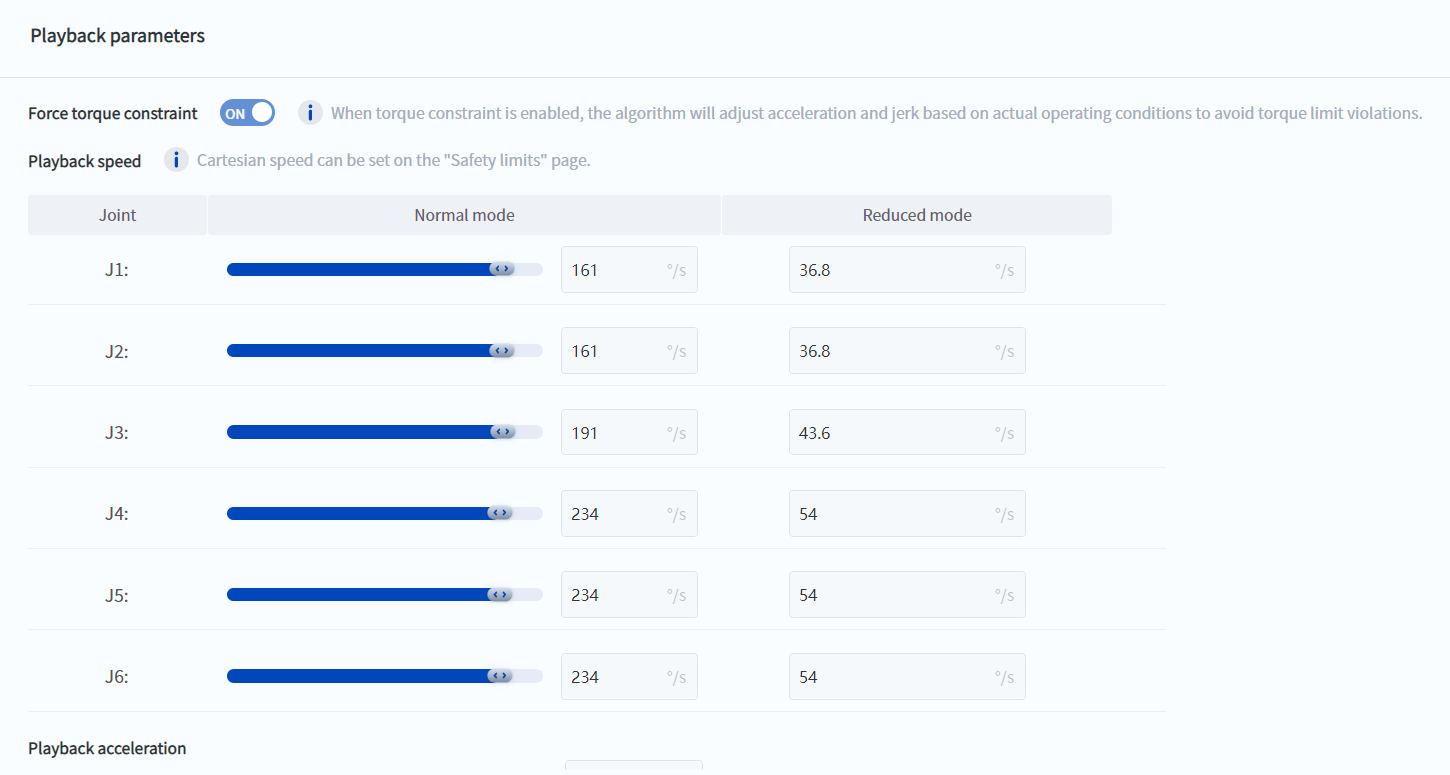
- Torque constraint function
- The torque constraint function is enabled by default when the robot leaves the factory. The robot acceleration is automatically adjusted during the movement so that each joint does not exceed the allowable torque of the joint. Even if unreasonable movement parameters are set, the reliability of the reducer can be guaranteed.
- This function can also improve the robot's work cycle: when the robot's movement parameters are increased and the torque constraint function is turned on, there is always one joint at the maximum allowable torque during the robot's movement, and the overall work cycle is the highest.
- Changes to the protection stop function
- To ensure the safety of the robot, in any state after the protection stop is triggered, the robot will no longer be allowed to start or continue program operation (including trajectory reproduction)
Key Features
- Trajectory recovery function
- Program debugging function
- Force control plug-in
- File migration function
- One-click upgrade function
- Custom pop-up window instructions
- Robot jog operation is more convenient
- TCP secondary development function optimization
- Robot usage time limit
- Load automatic identification accuracy improvement
- Single-axis zero point calibration
- Rich building block programming functions
-
Specific Feature Description
- Trajectory recovery function
- The robot enters the pause state when an alarm is triggered (such as emergency stop, command error, etc.). Restarting the program can continue to run along the original trajectory, reducing downtime, quickly resuming operation, and ensuring continuous production.
- Allow the robot to support jog or drag in the pause state. At this time, click Continue to run and the robot will move slowly to the pause position and then continue to run.
|
|
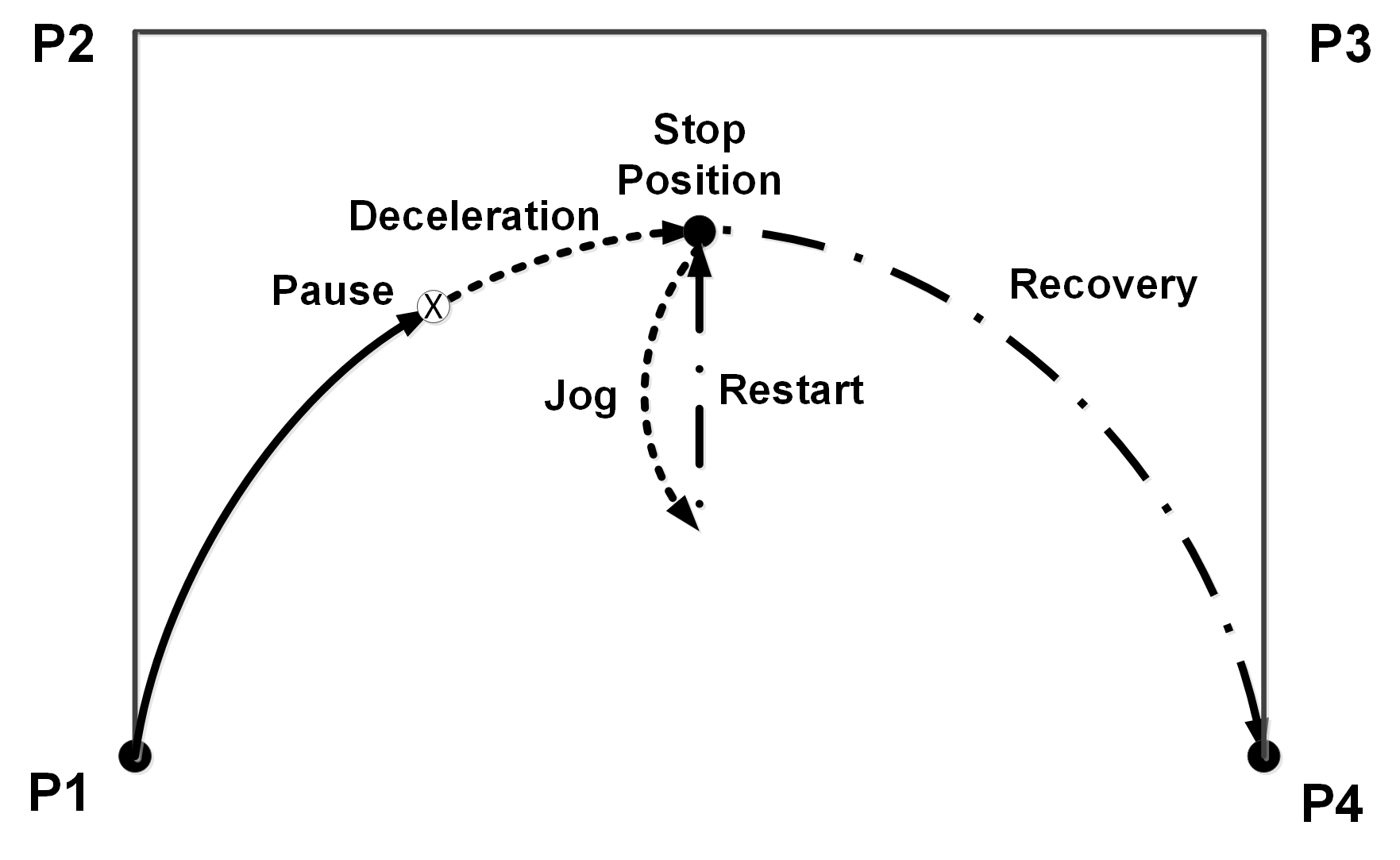
In the motion procedure of the robot along the P1-P2-P3-P4 trajectory:
- The robot is triggered to stop at the "pause" position, and after a period of deceleration, it finally stops at the "stop position"
- At this time, the robot can be moved to a safe position by jogging or dragging
- After solving the problem, restart the robot, the robot will move slowly to the final "stop position" after the pause, and then continue to run along the original trajectory
|
*Note: This function is not effective by default. You need to enable it in the upper computer "Settings-Advanced Settings-Advanced Functions-Support Jog in Pause State"
When restarting the movement, the teaching interface will prompt that the robot trajectory has deviated. You can choose to manually jog the robot to the stop position to ensure that the restart action will not interfere with other devices.
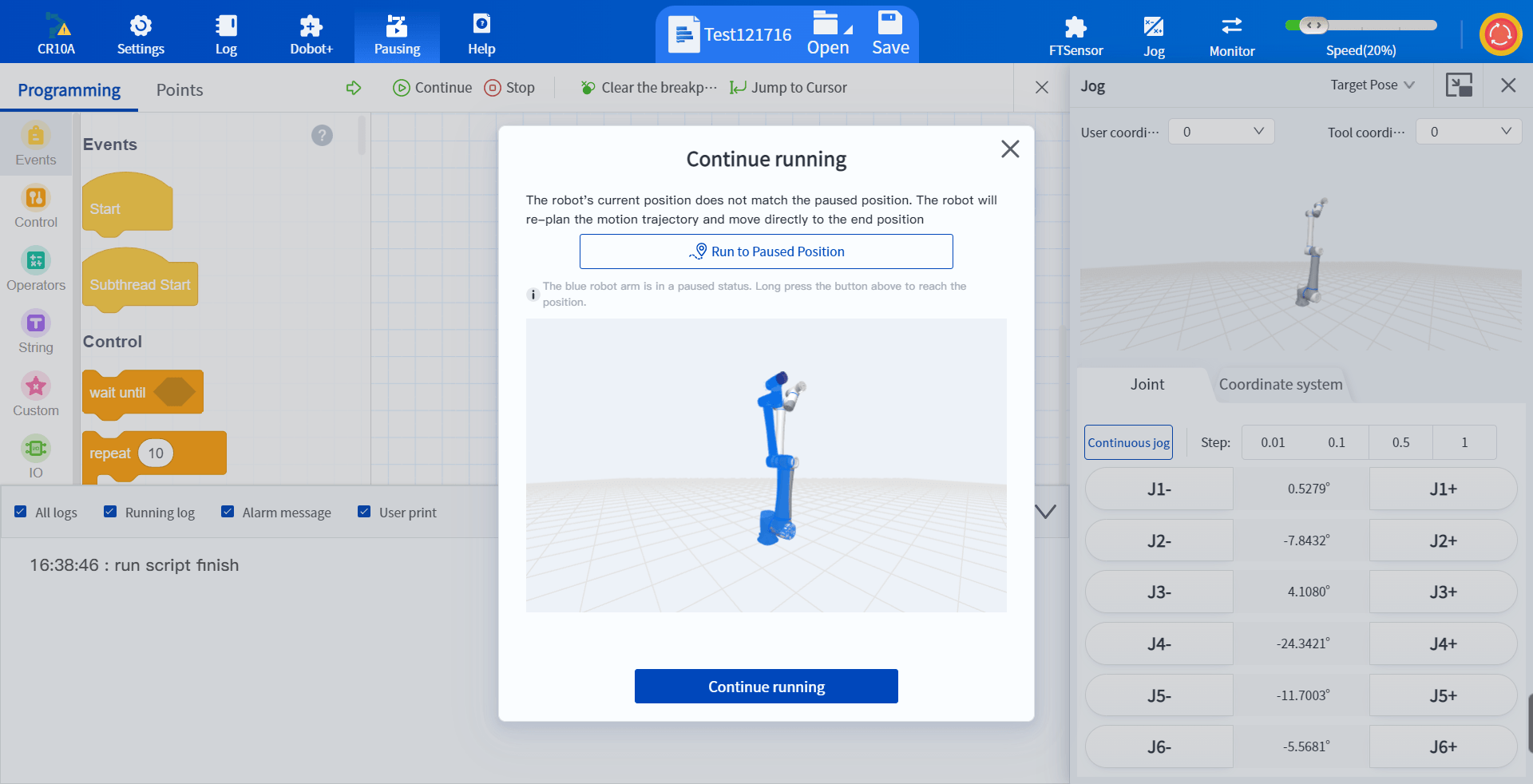
- The "Apply" icon at the top of the software can be used to determine whether the robot is in a paused state, which will help you determine the possibility of the robot continuing to run. At the same time, in the paused state, the robot program cannot be edited and the parameter settings cannot be modified. This icon can also deal with this problem to a certain extent.
|

The robot is in stopped state
|

The robot is in program running state
|

The robot is in program pausing state
|
- Program debugging function
The version has systematically optimized the existing debugging functions, and can perform arbitrary line start, breakpoint, and single-step debugging, which improves the program debugging efficiency by more than 25%.
- The "Run from selected line" or "Single-step from selected line" function will allow the robot to skip the program segment before the selected line and start running the program from the specified line. It is very convenient when debugging the middle line of the program. For example, if you have re-taught certain points, you need to re-test to confirm the effect.
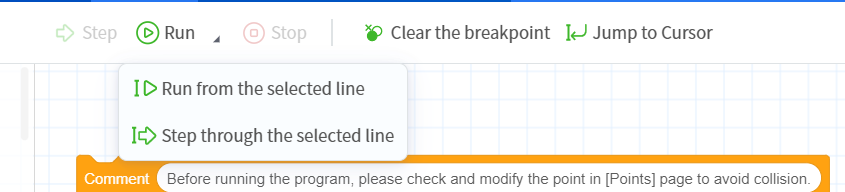
- Single-step function allows the robot to run the command program line by line, which is convenient for accurately locating problems. It should be noted that the robot can only perform single-step debugging when it is in the pause state.

- Breakpoint debugging function: When the robot runs to the breakpoint line, it will automatically pause the program. Through the combination of "breakpoint" + "single step" debugging, first breakpoint rough screening, then single step fine tuning, debugging efficiency can be improved by more than 40%.
|
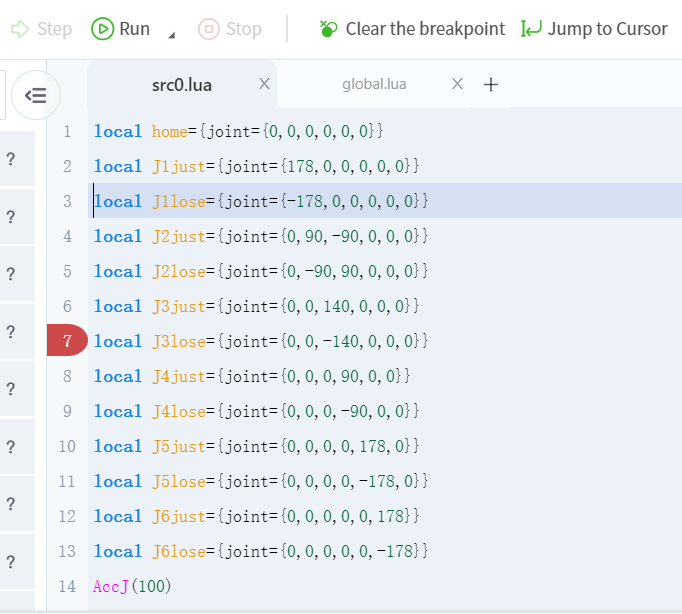
Add breakpoints in script programming
|
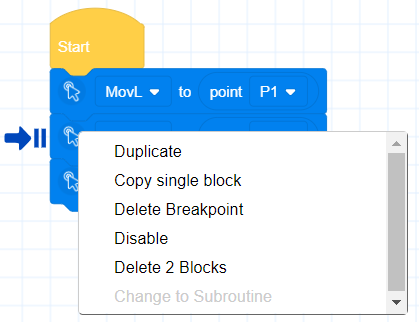
Add breakpoints in blockly programming
|
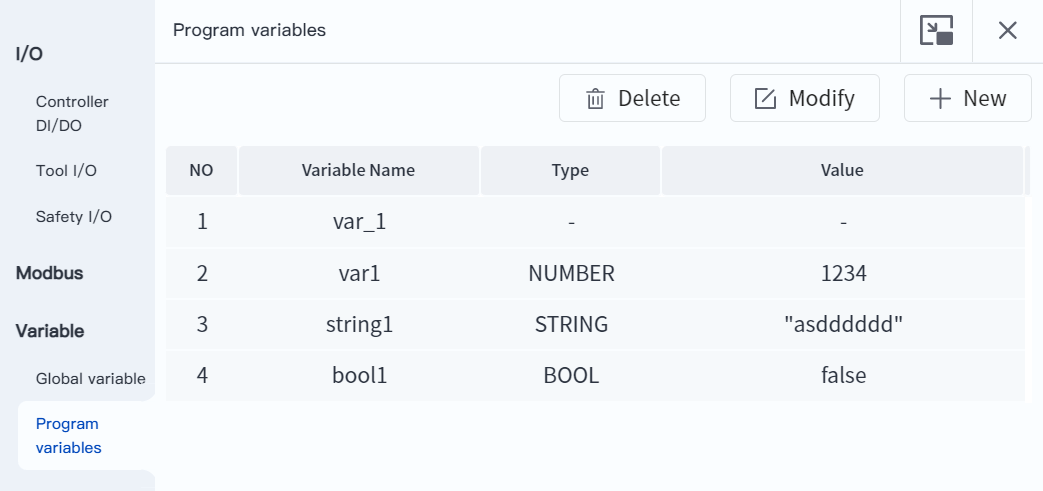
- Supports real-time monitoring of variables. Enter the "Monitor-Variables-Program Variables" interface and freely add variable names to be monitored. Program code debugging combined with real-time variable monitoring can accurately locate the root cause of the problem.
- Force control plug-in
A new six-axis force sensor plug-in is launched to meet the needs of conventional force control applications and solve complex tasks in high-precision, high-flexibility and high-safety scenarios.
- Force-controlled dragging function
- Based on the dragging of high-precision six-axis force sensors, the dragging starting force can be reduced to 3N, greatly improving the robot's dragging compliance and dragging efficiency
- The dragging direction can be set, and different dragging directions can be selected according to different scenarios to further improve the dragging efficiency. For example, in the teaching points of glue application, the robot can be constrained to only translate to ensure that the TCP posture will not change during the dragging process, ensuring the glue application effect.
- Supports dragging direction constraints based on the tool coordinate system or the user coordinate system to improve dragging flexibility.

- Force control compliance function
- Through real-time force feedback, millimeter-level precision control is achieved to meet the needs of applications such as constant force grinding and constant force pressure holding
- Supports real-time modification of elastic coefficient, damping coefficient, and rigidity coefficient. Different compliance control parameters are selected according to the material, fixing method, contact position, etc. of the contact object to achieve the best force control effect.

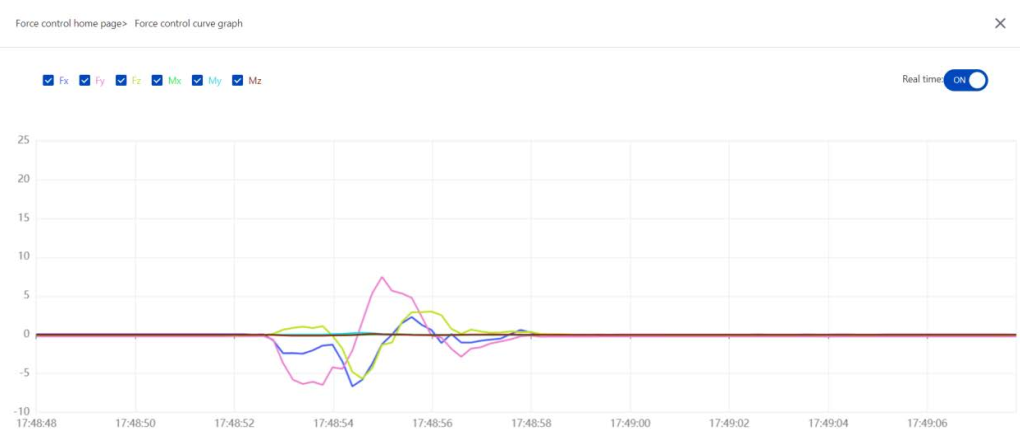
- Supports real-time curve display of force data, which can accurately view the specific values of force control in various directions at different times, and transform abstract force perception into visual data insights, making it easy to compare force control effects under different parameters, or quickly locate force control anomalies (such as overshoot, fluctuation)
- File migration function
This version provides a "file migration" function, which can batch copy the files and parameter settings of one robot to another robot, including engineering files, IO configurations, safety parameter settings, motion parameter settings, etc., and can import and export each type of file separately. When users are carrying out batch production of equipment, they can complete the equipment parameter configuration with one click, and the time is shortened to less than 1 minute.
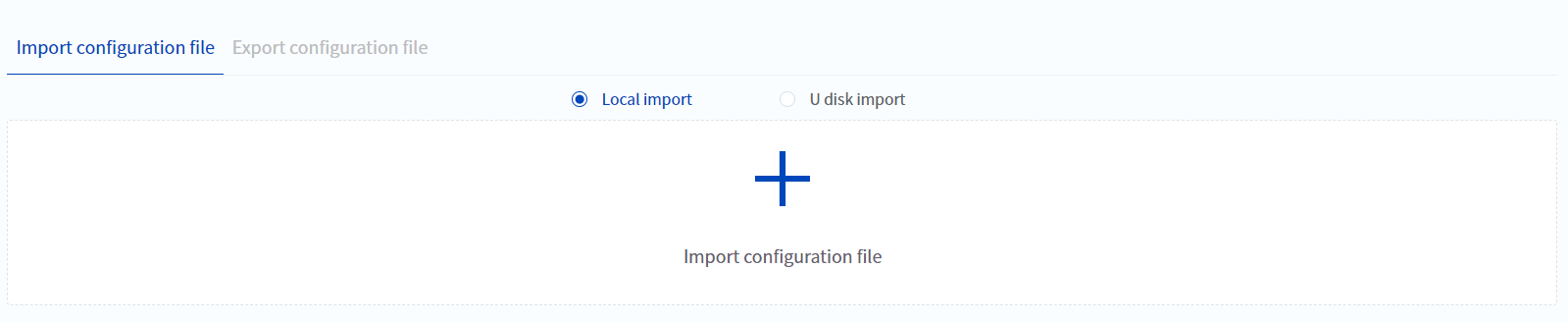
- If necessary, it can also meet the functional scenarios of file backup and file recovery. Regularly export the current file. When the program or parameter settings are lost or tampered with due to misoperation, the robot can be quickly restored to the last backup state by importing the backup file.
- One-click upgrade function
- The robot controller firmware and slave firmware can be upgraded with one click through DobotStudio Pro software, which is more flexible and convenient.
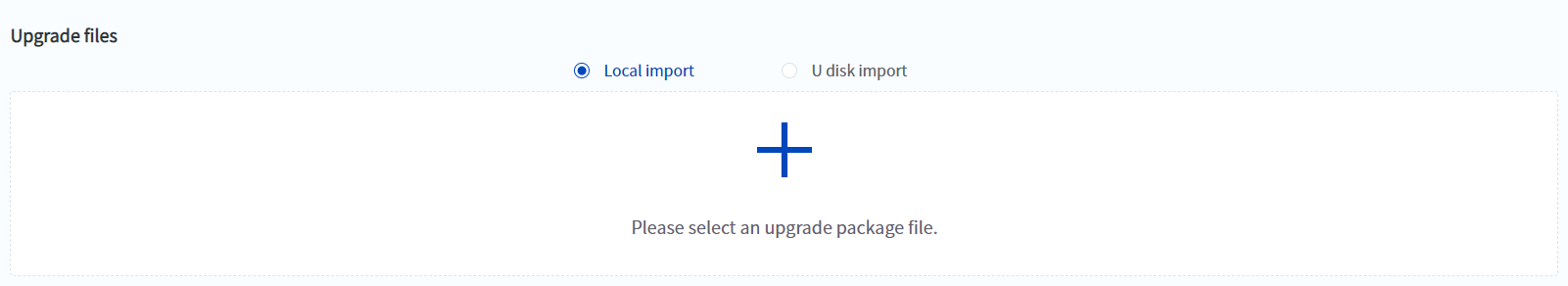
*Note: This function is only effective when the current version is 4.6.0.0 or above, and can only be upgraded to 4.6.0.0 and above
- Custom pop-up window instructions
- When executing this command, the robot will pop up a window and pause the program execution. The window content supports user customization.
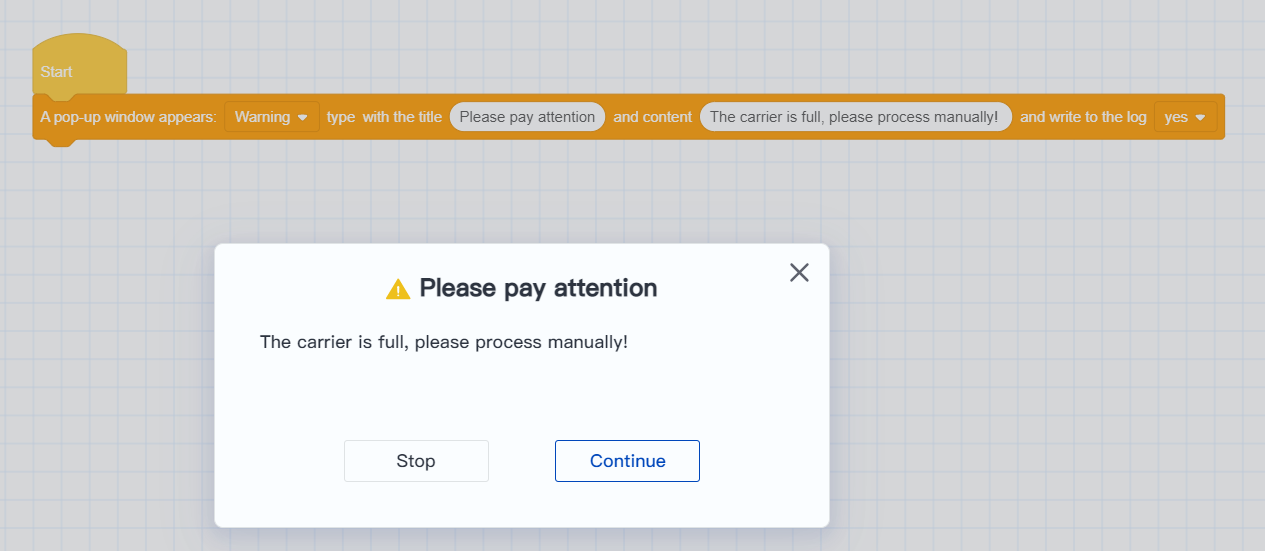
- You can choose to write the pop-up content into the robot log to facilitate querying and tracing historical production data and abnormal status.
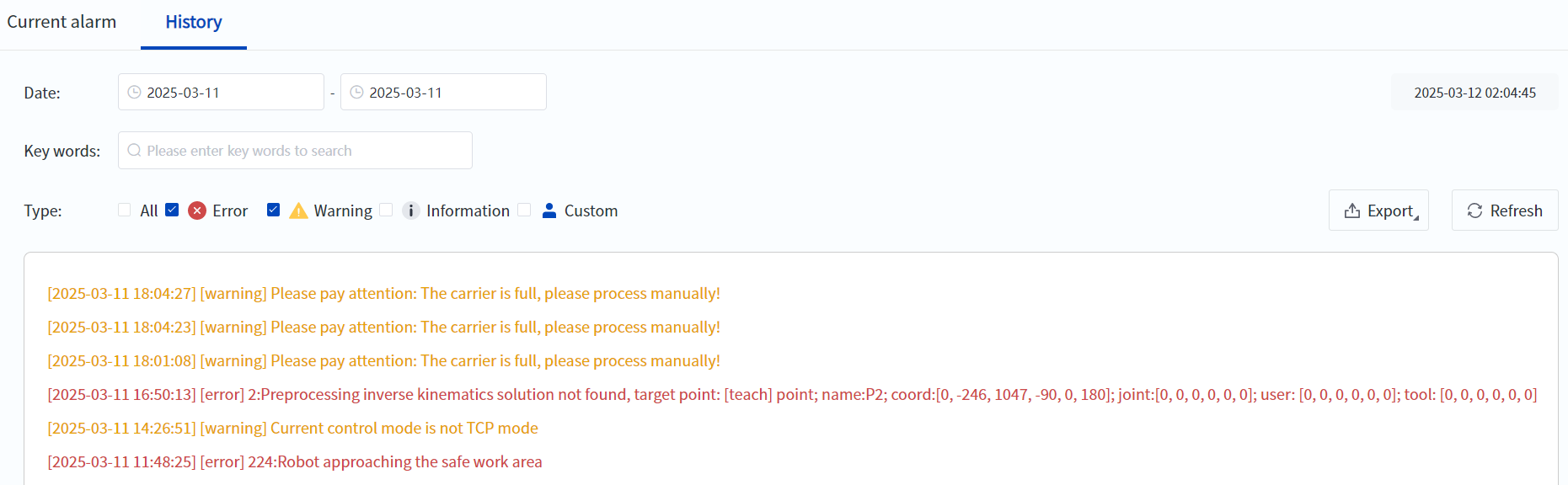
- With the newly added "stop program" command, the user-defined alarm function can be realized, that is, the robot automatically ends the program after processing the pop-up content

- Robot jog operation is more convenient
- The interaction of jogging to the target position is clearer. The robot's target position is displayed as a blue model, allowing users to intuitively understand the target position of the movement and predict the robot's movement path, identifying possible collisions or unreachable risks in advance.
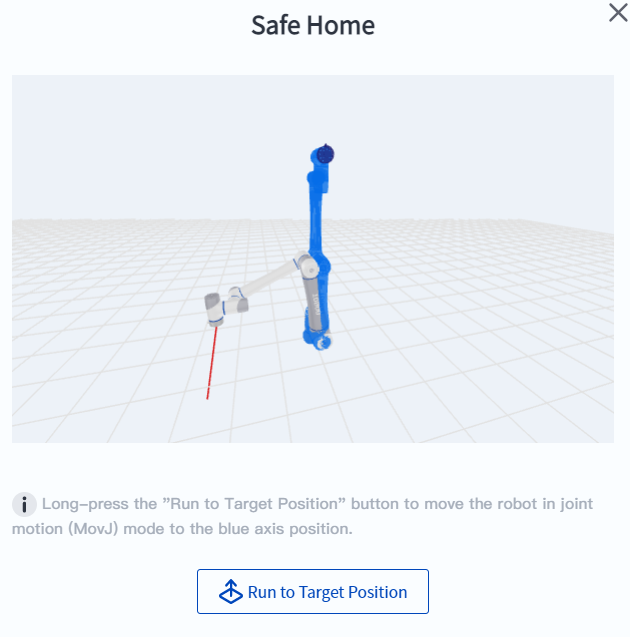
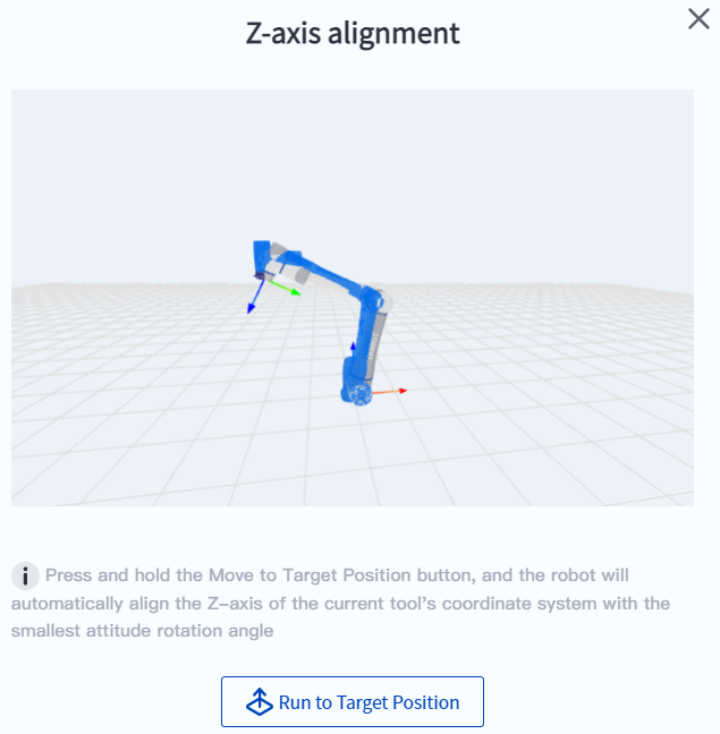
- Z-axis alignment. The robot automatically aligns the Z-axis of the current tool coordinate system with the Z-axis of the current user coordinate system at the smallest posture rotation angle. In many scenarios (such as palletizing, locking, desktop handling, etc.), horizontal grasping can be quickly achieved without fine-tuning the robot angle.
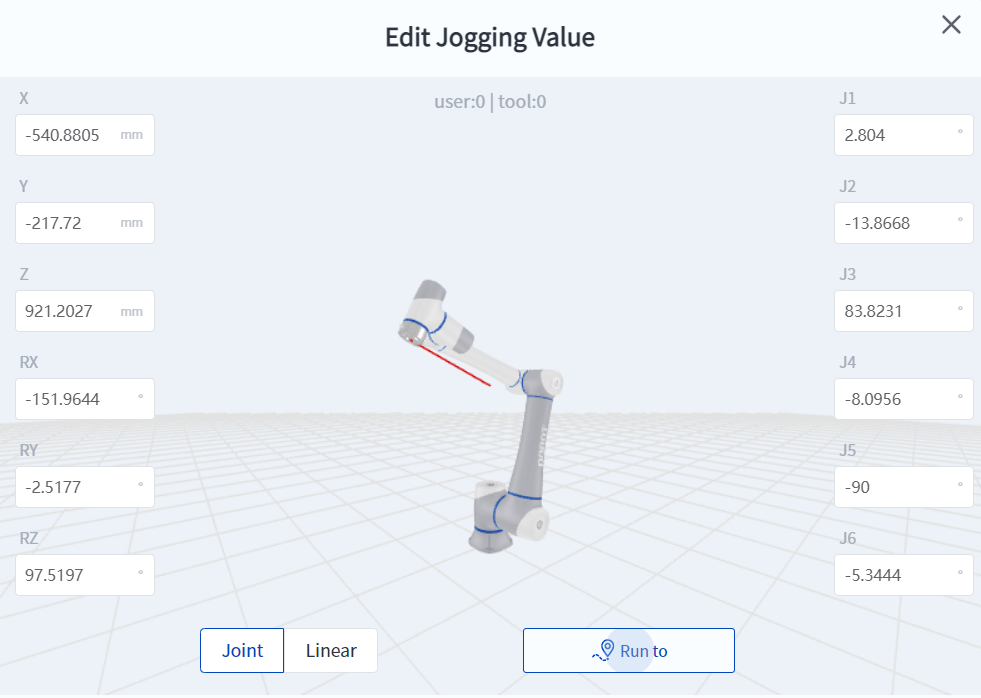
- Manually input coordinate values for jogging. You can directly input the robot's joint coordinate values or Cartesian coordinate values for jogging.
- TCP secondary development function optimization
- In online mode, the robot can be switched to TCP mode through TCP commands. In this way, even if the DobotStudio Pro software is not connected, the robot can be switched to TCP mode for further control, improving the ease of use of the robot for secondary development.

- In remote TCP mode, you can also view the robot's IO, variables, etc. through DobotStudio Pro software without switching the robot to online mode
- Feedback on the robot's safety status has been added to the real-time feedback port (30003~30006)

- Robot usage time limit
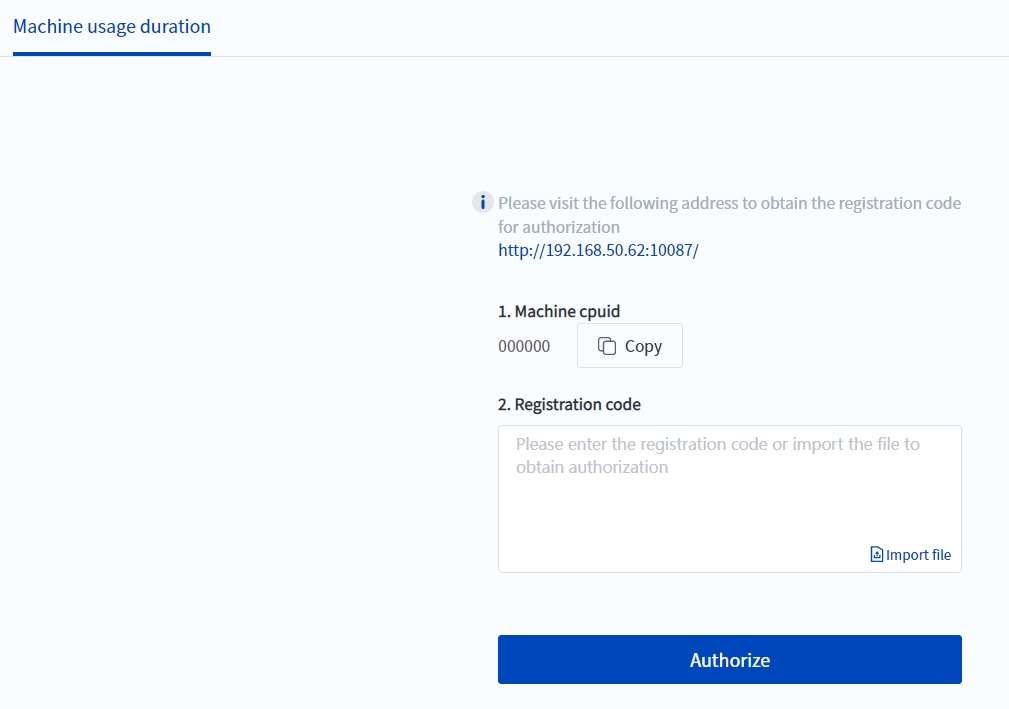
- The robot can be authorized for a certain period of time. When the specified period of time is exceeded, the robot will continue to report errors and the use of the robot will be restricted. This is meaningful for some scenarios, such as robot equipment rental business. However, it should be noted that this function can only be set in the manufacturer mode. If you need to use it, please contact DOBOT Technical Support.
- Load automatic identification accuracy improvement
- The automatic load identification scheme has been optimized, and the identification time has been extended (about 3 minutes), but the identification error can be reduced to less than 10%. In terms of actual user operation, the usage is exactly the same as the previous version.
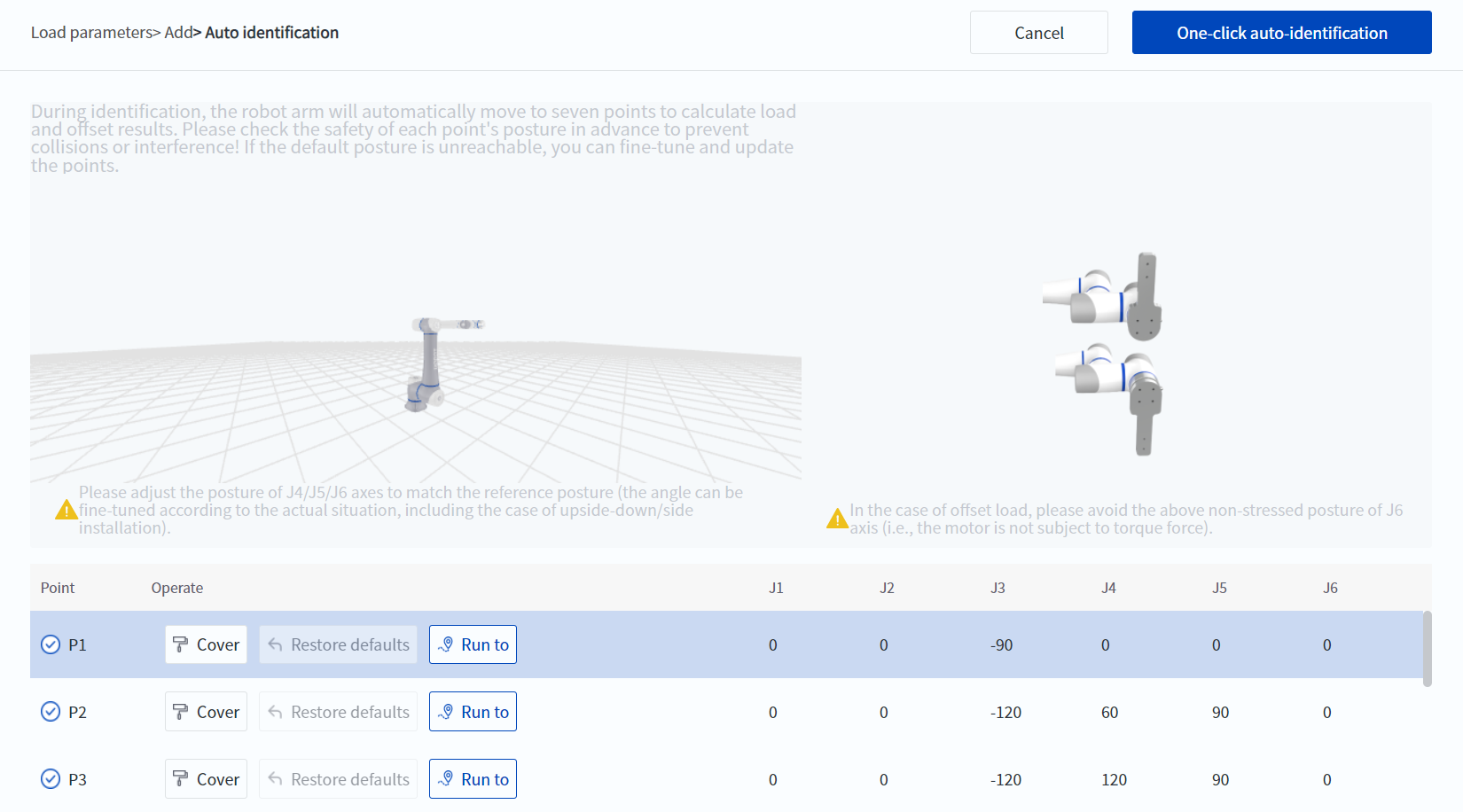
- Single-axis zero point calibration
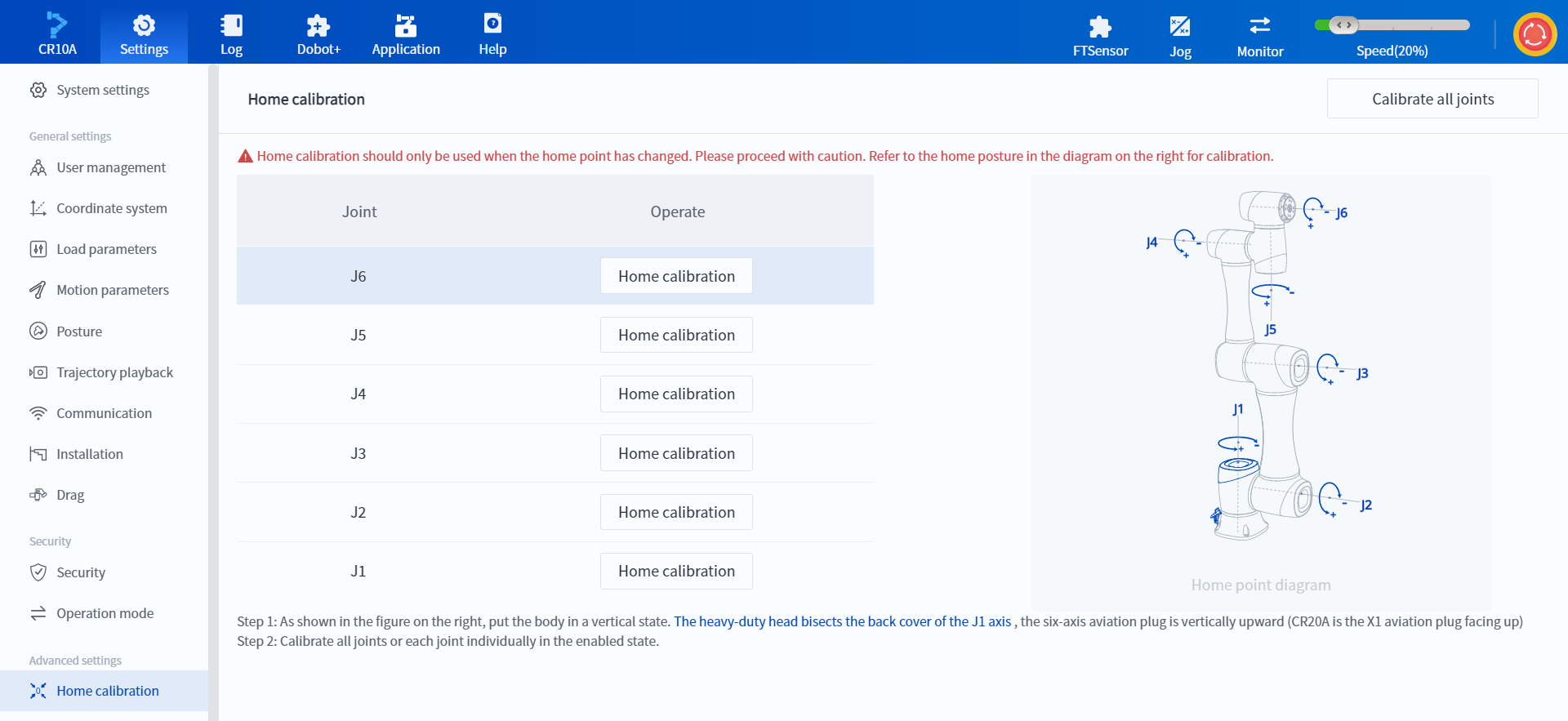
- When performing zero point calibration, you can save the zero point of a certain joint separately. When the robot's workspace is limited and all joints cannot be moved to the zero point position, the whole machine zero point calibration can be completed by calibrating each joint one by one.
- When replacing a robot joint and needing to calibrate the zero point of the joint separately, this method can be used to quickly complete it.
- Rich building block programming functions
- You can quickly add points to the building blocks or overwrite the current points without switching between the programming interface and the point storage interface, which improves the efficiency of point teaching
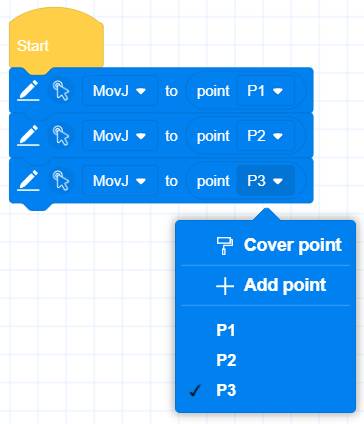
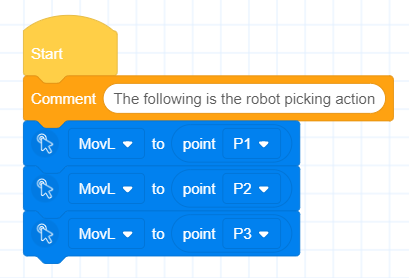
- Supports disabling and enabling of blocks
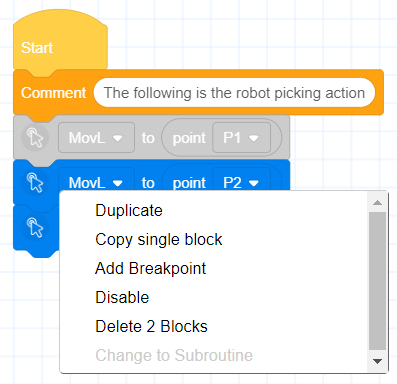
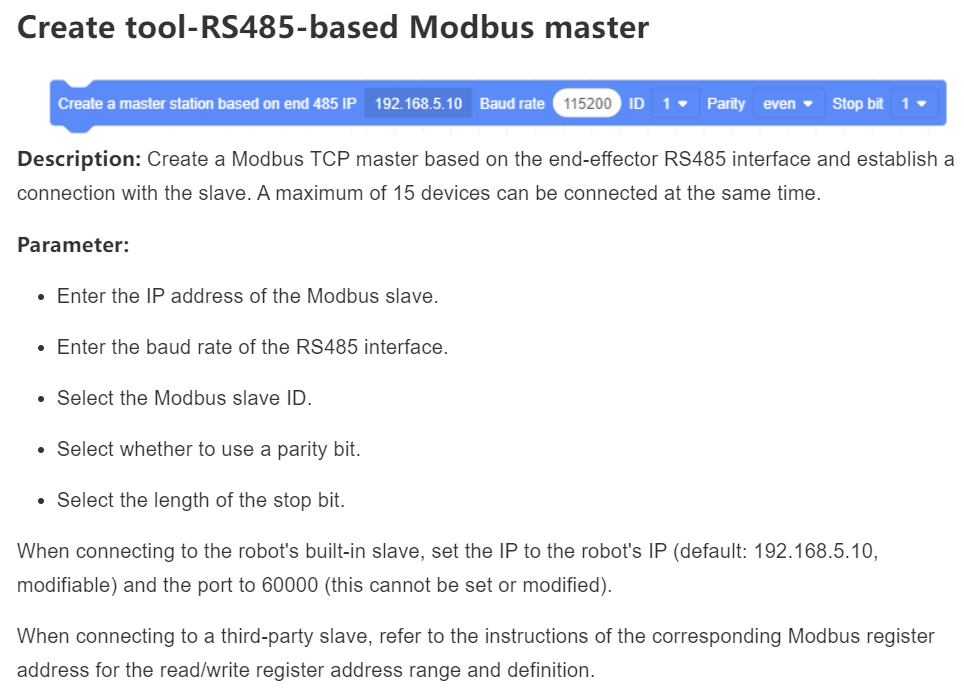
- Added Modbus master function building block based on RS485 interface at the end of robot body
UI Interaction
- Software homepage copy update: Safety IO and energy feeding board names changed to safety controller and power board
- Block translation update - Korean and German update
- Block Programming-Script Subroutine Optimization Edit Box
- Dobot+ Added the entry to view the plug-in matching table
Bug fixes
- Fixed the issue of "When the script is run at 100% global rate and moves toward the safety wall, joint movement failure alarm may occur occasionally"
- Fixed the issue of "When CR20A moves to the shoulder singularity point at low speed, servo error alarm may occur occasionally"
- Fixed the issue of "After the main thread ends or pauses, the child thread does not end or pause immediately"
- Fixed the issue of "In certain scenarios, the DO signal is automatically closed after the CR10A alarm"